If you’ve been shopping for a new car recently, you’ve likely come across the term “CVT” listed as the transmission type for many models.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Improved Fuel Efficiency | Driving Experience (lack of distinct gear shifts) |
| Smoother Acceleration | Reliability Concerns (premature failure, wear) |
| Compact Design | Noise and Vibration (under hard acceleration) |
| Lower Emissions | Limited Towing Capacity |
CVT stands for Continuously Variable Transmission, and it’s a type of automatic transmission that has been gaining popularity among automakers in recent years. But what exactly is a CVT, and what are its pros and cons? Let’s dive into the details.
What is a CVT Transmission?
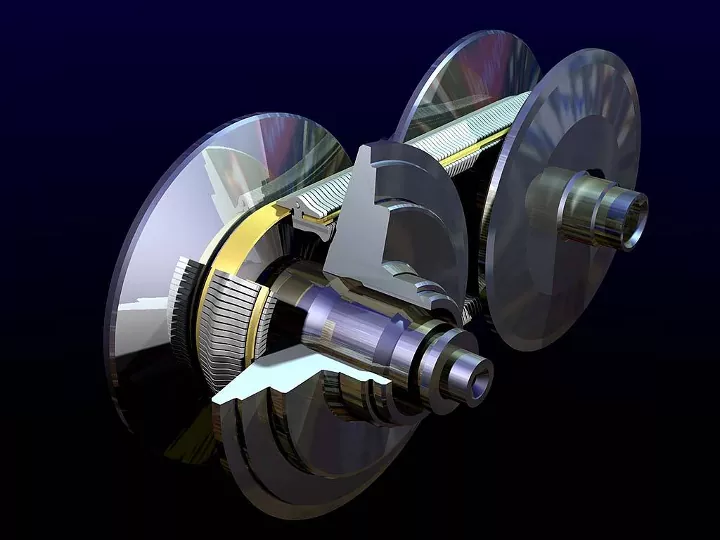
A traditional automatic transmission uses a set of gears that shift up and down to provide the appropriate amount of power and torque to the wheels. A CVT, on the other hand, operates using a pair of pulleys connected by a steel belt or chain. One pulley is connected to the engine, while the other is connected to the drivetrain. By adjusting the diameter of the pulleys, the CVT can continuously vary the gear ratio, essentially providing an infinite number of “gears” without any harsh shifts.
The Pros of CVT Transmissions:
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: One of the primary advantages of CVTs is their ability to keep the engine operating within its most efficient rev range. This results in better fuel economy compared to traditional automatic transmissions, especially in stop-and-go city driving conditions.
- Smoother Acceleration: Since CVTs don’t have distinct gear shifts, the acceleration is smoother and more linear. This can make for a more comfortable and refined driving experience, particularly in urban environments.
- Compact Design: CVTs tend to be lighter and more compact than traditional automatics, which can contribute to better overall vehicle efficiency and packaging.
- Lower Emissions: By keeping the engine operating at its most efficient RPM range, CVTs can help reduce emissions compared to conventional transmissions.
The Cons of CVT Transmissions:
- Driving Experience: While the smooth acceleration can be seen as a pro, some drivers find the lack of distinct gear shifts and the “rubber band” feeling of a CVT transmission to be less engaging or enjoyable compared to traditional automatics or manual transmissions.
- Reliability Concerns: CVTs have had some reliability issues in the past, with reports of premature failure or excessive wear on the pulleys and belts/chains. However, many manufacturers have been working to improve the durability and longevity of their CVT designs.
- Noise and Vibration: Under hard acceleration, some CVTs can produce a distinct “drone” or elevated noise levels due to the high RPMs required. Additionally, the steel belt or chain can sometimes cause vibrations to be transmitted into the cabin.
- Limited Towing Capacity: Due to their design, CVTs generally have lower towing capacity ratings compared to traditional automatics or manual transmissions.
The Technical Nitty-Gritty:
CVTs rely on a complex system of pulleys, belts/chains, and hydraulic actuators to continuously vary the gear ratio. The primary pulley is connected to the engine, while the secondary pulley is connected to the drivetrain. By adjusting the diameters of these pulleys using hydraulic pressure, the effective gear ratio can be changed seamlessly.
One of the challenges with CVTs is managing the high tension loads on the belt or chain, which can lead to premature wear or failure. Manufacturers have adopted various strategies to address this issue, such as using specialized materials, improved lubrication systems, and advanced control algorithms.
Another technical consideration is the transmission’s ability to handle high torque loads, which is why CVTs are often paired with smaller, more efficient engines rather than high-performance powerplants.
The Future of CVT Transmissions:
As automakers continue to prioritize fuel efficiency and emissions reduction, the development of CVT technology is likely to continue. Some manufacturers are exploring hybrid or electrified versions of CVTs, which could further improve efficiency and performance.
Also Read:
- Top 5 SUVs Without a CVT Transmission – SuvExtreme
- The Truth About CVT Transmission Reliability
- Understanding DSG Transmissions – The Future of Shifting Gears
- Transmission Overheating: The Root Causes and How to Prevent It
- The ZF 8-Speed Transmission: A Masterpiece of Efficiency and Performance
- Why is My Car Leaking Oil When Parked?
Additionally, advances in materials science and control systems may help address some of the reliability and NVH (noise, vibration, and harshness) concerns associated with CVTs.
Ultimately, the decision to choose a vehicle with a CVT transmission will depend on your driving preferences and priorities. If fuel efficiency and a smooth ride are top concerns, a CVT could be an excellent choice. However, if you value a more engaging driving experience or plan to do frequent towing, a traditional automatic or manual transmission might be a better fit.
As with any major vehicle component, it’s important to do your research, read reviews, and consult with knowledgeable sources before making a decision. And remember, proper maintenance and adherence to the manufacturer’s recommended service intervals can help maximize the lifespan and reliability of any transmission, including CVTs.


[…] CVT Transmission: The Good, The Bad, and The Technically Advanced […]